The energy rating allows comparing the energy consumption and CO2 emissions of a building with buildings of similar characteristics and location. It is a clear indicator of the state of the building, as a good energy rating is a clear indication that a building is well maintained.
Buildings are large energy consumers, as HVAC systems and hot water are necessary to maintain their comfort conditions. It is estimated that they consume just over 30 % of final energy and are responsible for one third of carbon dioxide emissions in Spain, according to the IDAE. Just like with appliances, the energy certificate of a home provides the consumer with objective information about its energy consumption compared to other buildings, and the better the construction characteristics of the enclosures and the envelope, the better the energy rating will be.
What are energy efficiency certificates, how and by whom are they prepared, and what do they take into account? Let's look at some of these basic issues to better understand the energy certificate and how the energy rating of a property can be improved.

What is an energy certificate?
The energy certificate is a calculation method carried out using applications approved by the Ministry. From data taken from the project or from a visit to the building, it is possible to estimate its energy performance compared to other similar buildings. It thus provides the person interested in buying, renting or renovating a property with useful information about its energy characteristics and the approximate annual energy expenditure.
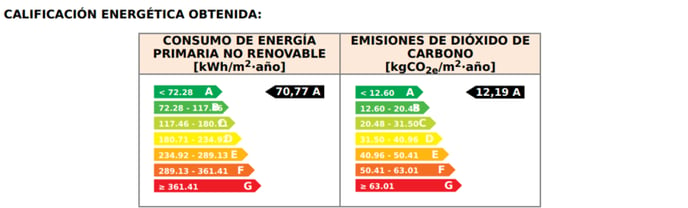
It contains a scale ranging from "G" to "A" depending on the CO2 emissions to the atmosphere and the energy use of the building, with G being the least efficient and A the most efficient. Additionally, it must include a proposal of measures to improve the energy rating of the property. Measures or actions like the ones we will see a little later in this article. An energy efficiency certificate is carried out by a competent technician, i.e. a registered owner who can guarantee its validity.
How are energy certificates produced? What do they take into account?
The aim of the energy certification is to promote energy efficiency in the real estate stock by retrofitting the existing building stock, constructing new buildings with higher energy requirements and using renewable energies. All of this serves to minimise energy needs and reduce their carbon emissions. The Energy Certification of Buildings came into force in 2013. According to the provisions of Royal Decree 235/2013, since 1 July 2013 it has been compulsory to issue these certificates for the sale and rental of new and existing homes in Spain. A building or dwelling without a certificate or with a certificate in progress may be indicative of a dwelling in poor condition or with hidden defects.
The aspects taken into account when calculating the energy rating of buildings are multiple: current regulations in building, the geometry of the building, the climate zone where the property is located according to the CTE, the 'skin' of the building, facilities integrated into the dwelling, facilities with renewable energy sources... Although, all of them can be grouped into two main categories:
- Energy consumption of the building.
- CO2 emissions from generating the energy it needs.

Actions to improve the energy rating of buildings
An efficient A-rated building uses up to 90% less energy. The following are some of the measures that can be taken to improve the energy rating of the house:
- Repair facades and improve thermal insulation (building envelope).
- Change the joinery.
- Analyse the most appropriate technologies for each project.
- Replace home heating equipment with more efficient ones, such as condensing boilers, heat pumps or heat recovery units.
- Incorporate renewable energies such as solar panels, thermal or photovoltaics for self-consumption.
- Use more efficient LED lighting.
What advantages does an efficient building have?
Improving the energy rating of a property, making it more efficient, and certifying such efficiency entails a series of advantages such as:
- Differentiation factor with respect to other properties ("green" image).
- Increased market value of the property.
- Reduced consumption of energy and, therefore, cost savings.
- Tax savings. The most energy efficient or energy saving houses have IBI reductions of up to 20% (category A).
- Greater comfort and well-being for the users of the building or home.
The sustainability of our planet and the fight against climate change depends on ensuring the energy efficiency of buildings. In this regard, and in accordance with European regulations, from 2021 new buildings will have to be nearly zero energy buildings (nZEB); from 2019 in the case of public buildings. A nZEB building has zero or very low energy use and, moreover, this must come from renewable sources.
Improving the energy rating of buildings provides lower energy consumption and greater comfort for their occupants, among many other benefits for both the pocketbook and the environment. Renovating our home is an opportunity to make it more efficient and sustainable. Find out about possible government grants.


