To reduce the CO₂ emissions of a building, we need to understand the impacts it generates throughout its entire life cycle. For this, there are standardized calculation methods that allow measuring these emissions and establishing what we would call a «carbon footprint».
Reducing the carbon footprint is key to achieving more energetically efficient and sustainable buildings. In this article, we will see what the carbon footprint is and how it is calculated, in addition to the types of scope and their elements.
The carbon footprint, what is it?
The carbon footprint is the calculation of the total amount of greenhouse gases (GHG) emitted into the atmosphere as a result of an activity, such as building. This activity includes everything from the manufacturing of materials, the building construction, its use, and its end of life. This value is measured in tonnes of carbon dioxide equivalent (kg CO₂ eq.) emitted per square metre of building constructed.
How is the carbon footprint calculated? Example with the NetZeroLCA Tool
In the construction field, the carbon footprint of an asset can be calculated throughout its entire life cycle; that is, the GHG emissions generated by the building can be measured at each step of the building process, from the manufacturing of the construction materials to the end of its useful life. Passing through their transportation, raw material extraction, the use phase, recycling process, etc.
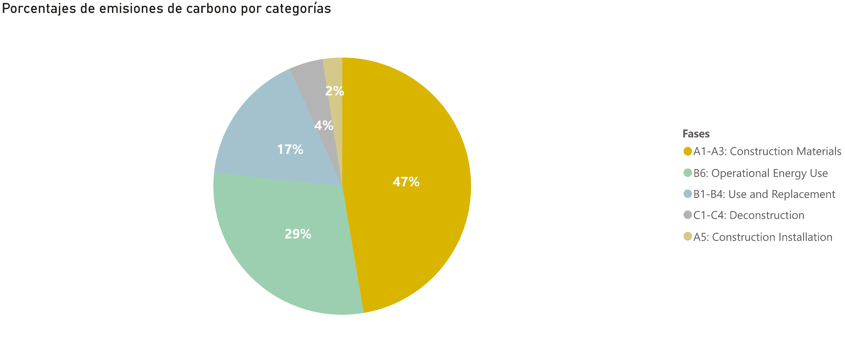
Although the scope of the study may be different depending on the data to be obtained, it is recommended to cover both embodied emissions (those that the building has accumulated during its construction process) and operational emissions (those that are released during the use phase of the building) in order to obtain a more accurate analysis.
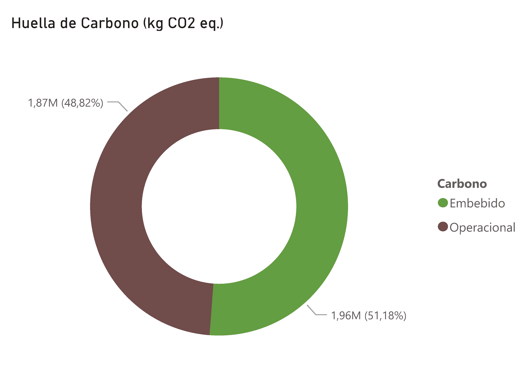
What is the tool used to measure the carbon footprint? Net Zero LCA is the tool developed by Zero Consulting that allows working from the early stages of design to reduce the carbon footprint of the building from a BIM model. This is adapted to the methodology of the different sustainability certifications (BREEAM, LEED, DGNB and VERDE) and has been approved by all of them.
The method of calculating the carbon footprint consists of connecting the BIM technology with the environmental data of the materials from the Net Zero LCA tool. That is, the measurements obtained from the BIM model are multiplied by the impact corresponding to each material defined in each environmental product declaration. This allows us to analyse the performance of materials within the building, quantify their impacts and compare them to benchmarks in real time.
Carbon footprint calculation. Step by step
The following is the methodology, the steps to follow, to reduce the carbon footprint of a building starting from a BIM model:
1. Define the scope of the study
First, the objective and scope of the LCA are defined.2. Extract the measurements of each material
From the BIM model, the measurements of all the materials to be evaluated in the project are extracted.
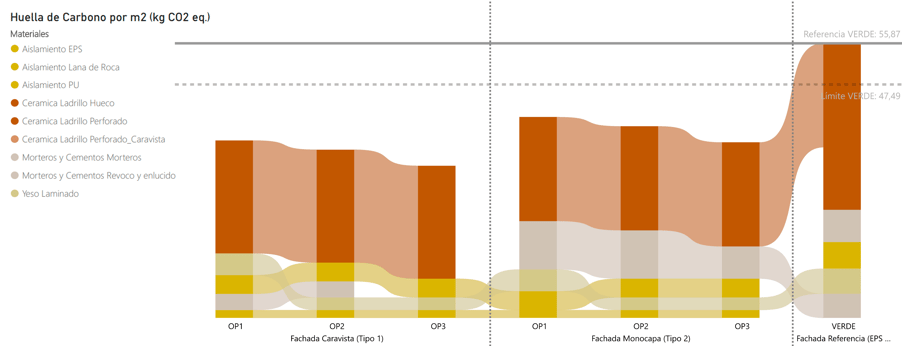
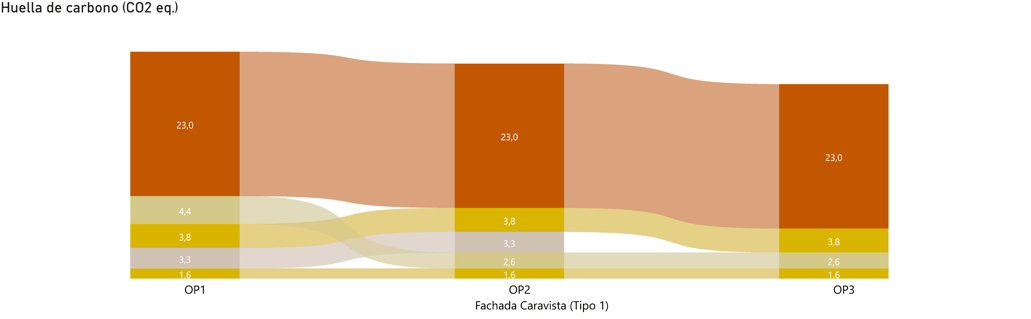
3. Reading of the information
The carbon footprint calculation tool reads the information defined in the building model.
4. Data entry
In the tool, data related to the building is selected and entered; these are:
- The lifetime of the building, which is the period for which the carbon footprint is to be calculated.
- Operational data: energy and water consumption.
- Other consumption during the construction phase.
- Characteristics of the transport of material from the manufacturing plant to the construction site.
5. Linking materials with the EPDs from the database
The materials defined in the BIM model are then linked to the environmental product declarations in the tool's database. This takes information from the main available open environmental databases online (international databases such as Ecoinvent, GaBi databases, Agri-footprint, ELCD, EU&DK Input Output database, Swiss Input Out database, and USLCI, among others).
6. Report generation and interpretation of results
Finally, detailed reports are obtained that allow the visualisation of the results obtained, the comparison of alternatives according to the selected project phases and the identification of the main sources of emissions, i.e. those construction phases or materials with the highest associated emissions. We can, in short, assess the best alternatives to optimise the whole carbon strategy of the building.
Once the carbon footprint has been calculated, the aim is to develop strategies to reduce or offset CO₂ emissions. One of the most important features of this methodology is the ease of generating multiple versions of a project to compare them with each other and facilitate decision-making.
In this article, we have seen how to calculate the carbon footprint of a building. This is measured in order to determine the CO₂ emissions that a building generates into the environment, to identify the environmental performance at each stage of the life cycle and determine strategies to reduce its impact. Therefore, the most effective time to carry out this type of analysis is at the beginning of the project.


