As technology advances, new options appear when it comes to building. Many of these technologies and innovations in construction contribute to achieving greater efficiency of materials and energy. Both by minimizing the environmental impact, as well as reducing waste and emissions due to transportation, among other factors, and reducing costs both in production and in the use of materials.
Let's look at some innovative technological applications in construction, their benefits, their relationship with sustainability, and future trends, for example, two technologies that can be perfectly combined: 3D Printing and the advancement of recycled materials.
3D printing as one of the innovations in construction
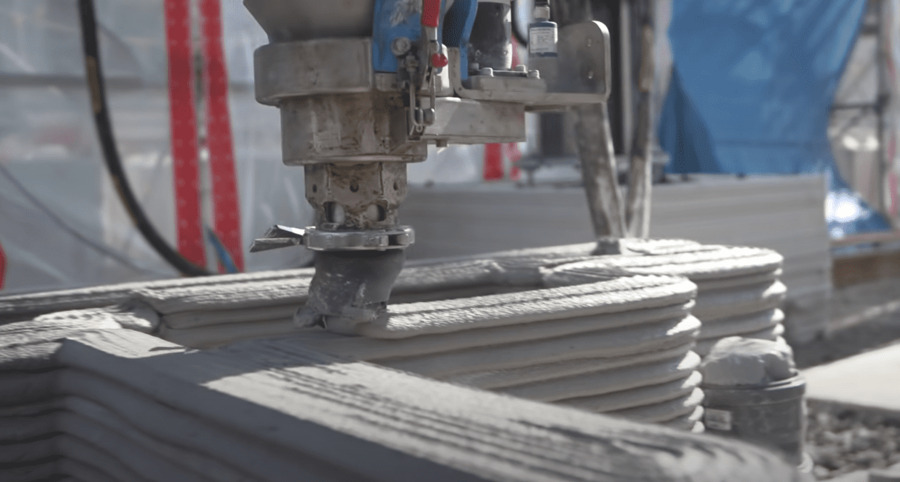
3D printing applied to construction makes it possible to create numerous elements: Specific components, complex structures, parts of buildings, construction solutions, walls, columns, decorative elements such as furniture, etc.
A 3D printer receives information on what to print via CAD or BIM software, and the machines superimpose the material according to the indications received. The materials used for these constructions are varied, but the most common is a mixture of concrete, geopolymers, fibre, and sand.
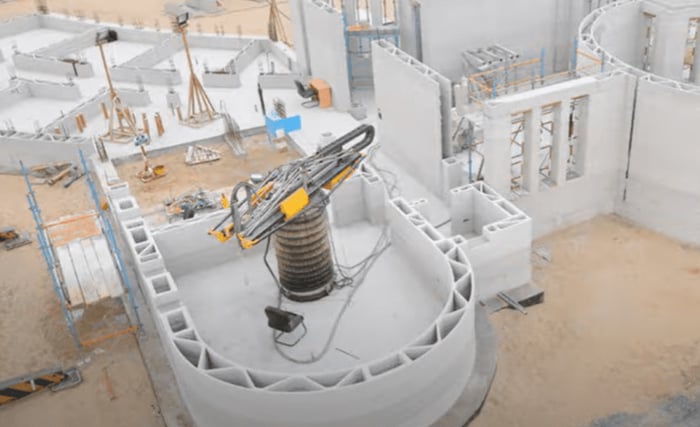

Compared to traditional techniques, the main benefits of this construction method are the reduction of waste generated, the reduction and optimisation of manufacturing time, the reduction of material and labour costs, and the possibility of not placing limits on the architect's creativity due to the flexibility that exists in the design.
All of this contributes to reducing the environmental impact generated by the building industry in the extraction of resources, the manufacture of its products and the construction itself, 3D printing offers solutions with a circular economy approach. Since it promotes the use of construction materials of organic base, eco-friendly products, and recycled materials. Moreover, by allowing the on-site construction of modular and complete buildings, emissions from the storage and transportation of materials are also reduced.
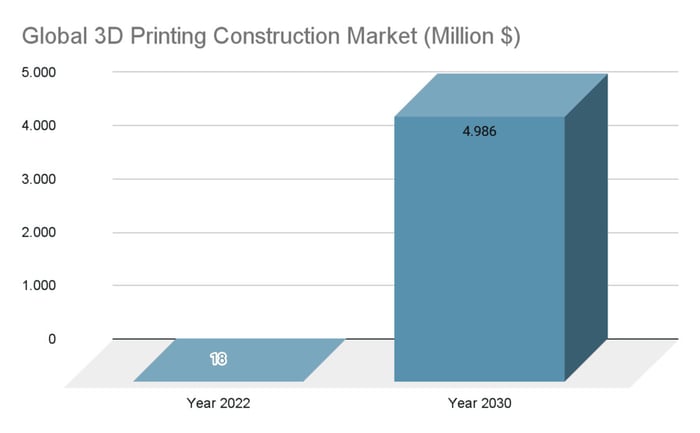
Advances in these technologies are steady, so much so that their value in the construction market is expected to reach up to $4 trillion by 2030, according to a study by Research and Markets.
It is an emerging business that will consolidate and could become a common solution, representing a sustainable and economical option in the real estate market.
How is artificial intelligence applied to building design?
According to the analysis developed by McKinsey in a recent study, AI is still rarely used in construction, but its development potential is demonstrated by the fact that several startups are betting on its implementation. This technology is another major innovation in construction, as it is opening up unprecedented possibilities, such as:
- The possibility of modifying structures and finding alternatives for the distribution of space. The starting point is found in the introduction of parameters and limitations, for example, that the floor of a building does not exceed a certain height, the type of materials, among others. Once the initial design is introduced, it is possible to change any element and have all other parameters automatically adapt to the modification.
- Design optimisers whose software, starting from an initial plan and using project parameters, performs an exhaustive analysis and calculates millions of different scenarios. Thus, the options are reduced to a few optimal alternatives that are carried out through a 3D model, to which the execution time is added.
- Analysis of images and videos of construction sites, where the main objective is to identify safety issues and reckless behaviour that can be addressed through training.
- Enhanced analytics platforms that collect and analyse sensor data to provide real-time solutions, cut costs, prioritise preventive maintenance and avoid downtime.
Innovative technologies applied to recycling and the use of recycled products.
The European HISER project (Holistic Innovative Solutions for an Efficient Recycling) is a demonstration project of circular economy principles applied to the entire building value chain. Their objective is to seek low-cost solutions with a holistic approach that allow for maximum resource utilization and waste reduction. This project, presented as another of the innovations in construction, consists of:
- Development of methodologies: the first aspect consists of the conjunction of methodological solutions and tools to control the types, qualities and quantities of materials to be used in the construction of a project and what the resulting construction and demolition waste will be. To achieve this, a material tracking system has been developed that allows for the classification of usable resources and the creation of an inventory of them.
- Development of technologies to produce high purity raw materials: once the quantity and quality of construction waste has been established, ways of recovering it are sought. The purpose is to produce raw materials with a purity between 80% and 100% through techniques of selection, crushing, and selective electro-fragmentation. This will be complemented with systems for analysing the quality of the raw materials obtained, which will be very important for the durability and reliability of the structures. It is estimated that these measures will be 20% more effective than usual recycling solutions.

- Use of new construction materials: After the production of raw materials resulting from construction waste, the aim is to replace or complement these raw materials with new materials. For example, with a cement whose carbon footprint is 10% lower than the current one, bricks with 10% recycled materials, or gypsum panels with 50% recycled materials, among others.
The development and implementation of innovative technologies in the building industry is changing the way we design and build. We are heading towards a future in which innovations in construction will allow us not only to reduce the costs and time involved in the sector, but also to commit to a more sustainable construction, which minimizes its environmental impacts and contributes to minimising climate change.