Smart Grids, also known as smart energy grids, are electricity grid systems based on advanced technologies that incorporate information and communication technologies. Bearing in mind that electricity supply is a basic need in any community, the development of Smart Grids presents a horizon of improvement in terms of bidirectionality, user information, metering and, of course, energy decarbonisation.
What is a Smart Grid?
A Smart Grid is an electricity network that integrates advanced information and communication technologies (ICT) to optimise the generation, transmission, distribution and consumption of electricity.
These smart grids enable bidirectional energy flow and contain a metering infrastructure that is self-healing, resilient to attacks, capable of predicting future behaviour and also able to respond to far-reaching circumstances.
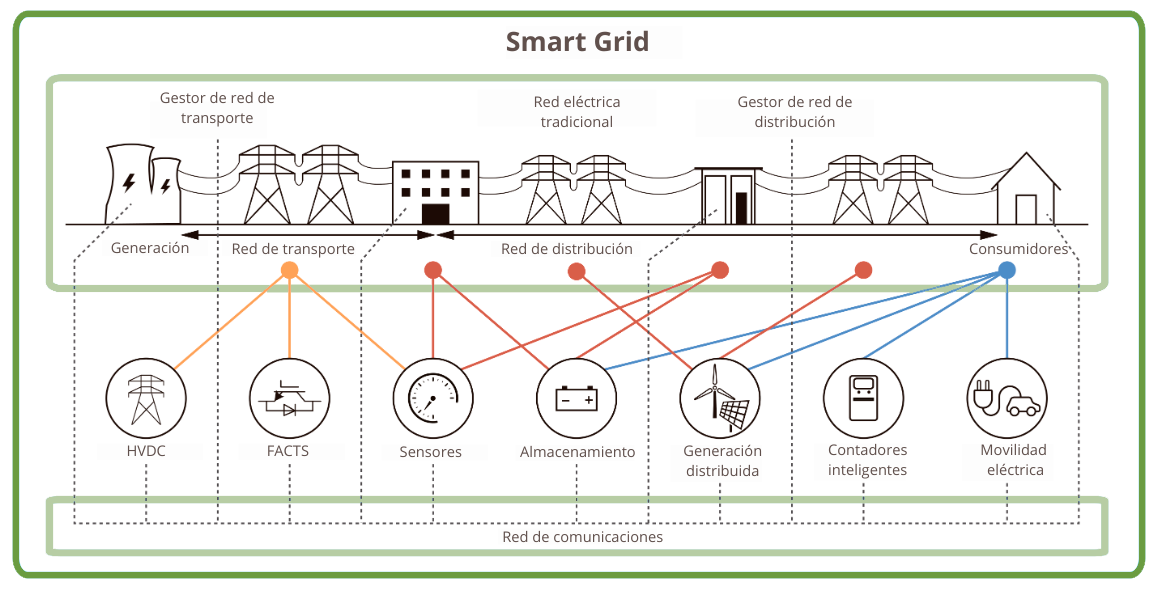
Structure of a Smart Grid. Source: ICAEN
Smart Grids contribute to sustainable urban development because:
- They provide information on energy use to final consumers.
- They make it easier for consumers to generate and consume their own energy.
- They improve the physical environment and the economic operation of the electricity system, reducing its losses.
- They help governments meet carbon reduction targets and provide economic stimulus to various sectors.
- They solve the main problems in the existing network, such as limited delivery, high cost of power outage and slow communications.
Finally, they are also an essential component in smart cities, as the supply of electricity is a basic need in any community.
Operation of Smart Grids
A Smart Grid uses smart devices such as smart meters for monitoring, smart energy storage devices, regulating devices for power quality monitoring, etc. A Smart Grid provides a bidirectional channel for energy transfer, as it can communicate with both conventional and non-conventional grids.
When designing and developing Smart Grids, we must ensure that it can contribute to:
- Decarbonisation of energy sources: Future energy sources must transition from fossil fuels to renewable energies such as wind and solar to reduce carbon emissions into the atmosphere.
- Improved efficiency in conversion processes and end uses: Smart Grids must significantly improve efficiency in all aspects of electricity generation, transmission, and utilization processes. End-use energy management helps energy to be used more efficiently through smarter management.
- Clean transport. Transportation represents a quarter of total carbon emissions in the United States and other advanced countries, only surpassed by electricity. Electric vehicles, along with future decarbonized grids, will help transform existing modes of transportation into clean and sustainable transportation.
Integration with renewable energy production technologies
Regarding the promotion of renewable energy sources, Smart Grids can contribute in several ways:
- Renewable energy integration: facilitates the integration of renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind, into the electricity grid. These technologies allow for better management of the inherent variability of these intermittent energy sources, which helps to balance the supply and demand of electricity.
- Demand-side management and energy storage: these allow for more active management of energy demand, which means adjusting consumption patterns to match the availability of renewable energy. Additionally, they facilitate the use of energy storage technologies, such as batteries, to store excess energy generated by renewable sources during periods of low demand.
- Smart grids: employ advanced monitoring and control technologies in electricity distribution networks, allowing for greater flexibility and adaptability. This is crucial for efficiently integrating distributed renewable energy, such as that generated by residential photovoltaic systems or local wind farms.
The importance of metering
 As mentioned above, metering plays an essential role in Smart Grids, and enables accurate monitoring of the system status. Smart meters are one of its central components and consist of sensing, computing, and communication subsystems. This type of element provides information about the loads, that is, about the energy flows of the network.
As mentioned above, metering plays an essential role in Smart Grids, and enables accurate monitoring of the system status. Smart meters are one of its central components and consist of sensing, computing, and communication subsystems. This type of element provides information about the loads, that is, about the energy flows of the network.
On the other hand, interoperability is a key factor in smart metering, and is necessary for a Smart Grid to function properly.
Smart Grids in decarbonisation
The decarbonisation of energy is a milestone on which many efforts are being made at international level, being one of the pillars of sustainability in the sector. The contribution of smart grids lies in the ability to manage the variability of renewable energies, optimise the operation of the electrical system, encourage the integration of electrification in key sectors, and promote energy efficiency through advanced monitoring and control of energy use.
These functionalities enable a transition to a more sustainable energy system, in which low energy consumption buildings play a key role, reducing greenhouse gas emissions and improving the efficiency of energy resource use.
In conclusion, Smart Grids represent a significant advance in the management and optimisation of electricity grids, offering a range of benefits from improved efficiency and reliability of energy supply to reduced carbon emissions. Its ability to integrate advanced information and communication technologies allows for smarter management of energy demand and supply, thus facilitating the transition to a more sustainable and resilient energy system.


